Note: There is an updated version of this article, which applies to the next generation of TimeXtender.
Before you attempt this you need to add the REST provider to your list of available sources.
Go through this guide before you start.
REST Information
A lot of companies stores data or gives access to data via an REST API. There are two setups in general JSON and XML. How these works can be seen in the JSON and XML cdata guides and they can be used to connect to the REST api with no changes to the methods.
Normally you connect to a web page URI with some link of some sort. Like this https://gorest.co.in/public-api/users, but you can also connect directly to a json/xml file, though it would be better to use the specific provider for that in that case.
CData Setup
Add a CData data source and point to the REST provider.
The first step in setting up a CData connector should always be to click the ? in the top right corner.
You have two data types of data.
XML
In general it is recommended to use JSON, but some XML rest providers exists.
The setup is the same, you add the URI or link to an XML file and synchronize. You can remove the access token to the Custom URL Params if you want, but doesn't need to do it. You can also move it to the RSD file, but read the guide for that to see how.
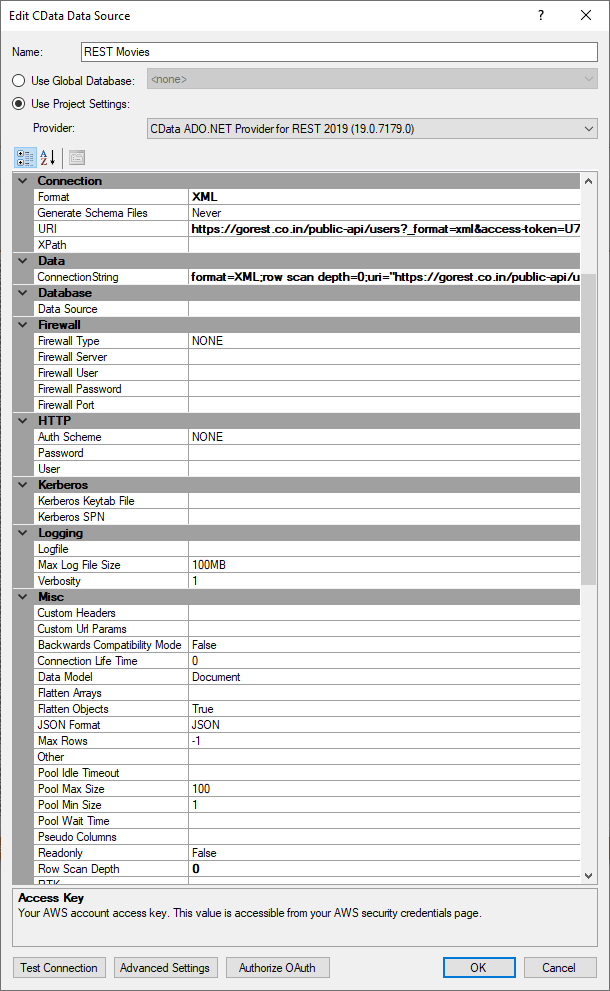
I also used row scan depth = 0 to be sure the whole document gets read.
JSON
Most REST api's use JSON. You can use most of the features also explained in the JSON CData guide.
So here are a list of good online api's to test on.
- REQRES - Test your front-end against a real API
- GoREST - Online FREE REST API
- dummy - Dummy Rest API example
- fixer.io - Online Currency data
Most of these have more or less the same setup, but done in different ways.
Here below I have gained access to GoRest. Go to the web page to get the access_token necessary.
Here is the uri i want to use and its contents
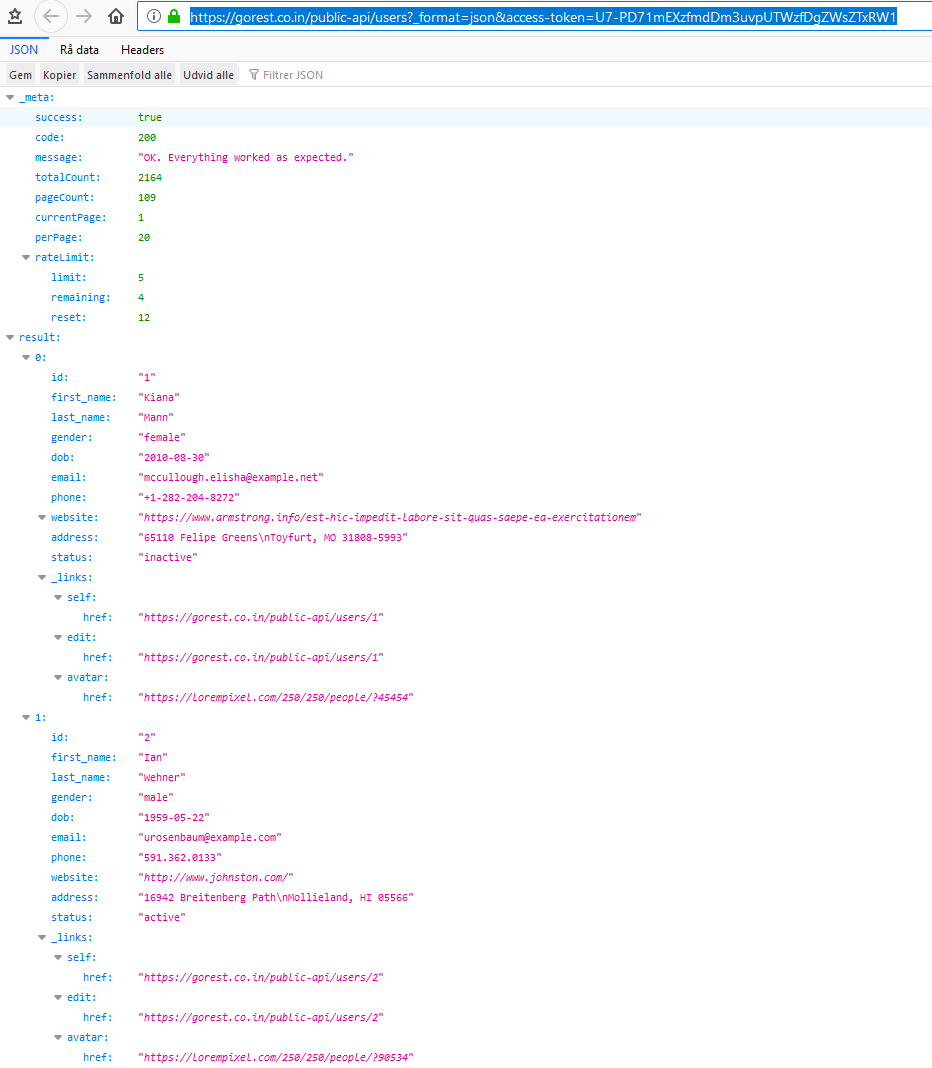
It gives me 20 rows from page 1 and needs a access token to work.
Here is how I set it up.
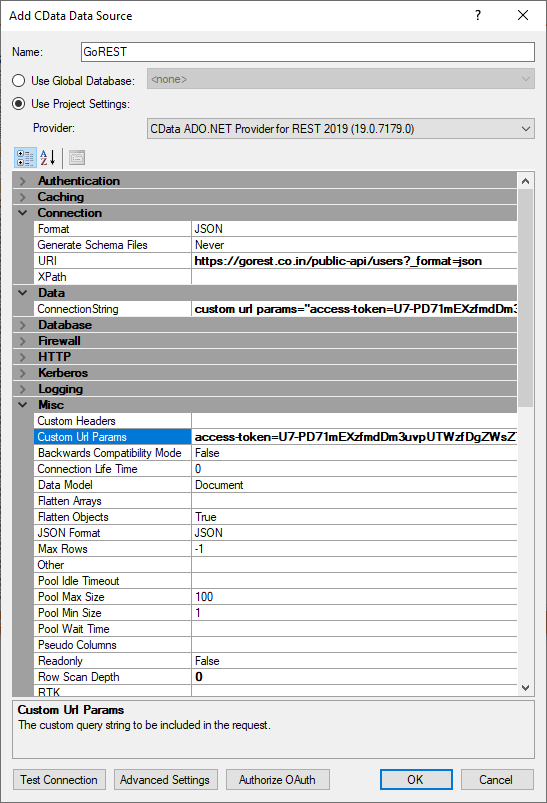
I added the access token to the Custom URL Params field, and you can add more options, you just need to know the code and set it equal to something, e.g. page=5 you just need to split it with a ; sign.
Getting access to the data
After this synchronize and you should be able to see the table. If you want to point to other tables in the api, e.g. posts instead of users. You can make it point to both tables.
Using a Custom Header
Sometimes it is a requirement to have some headers set to gain access. You can state them in that field. A common one is to set the text to be json with the following command.
Accept:application/json
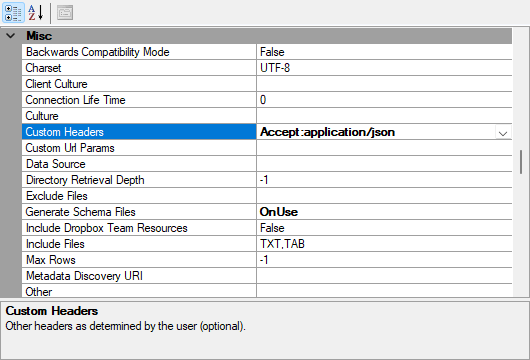
It is also commonly used to gain access with a bearer token like so.
Authorization:Bearer <token id>
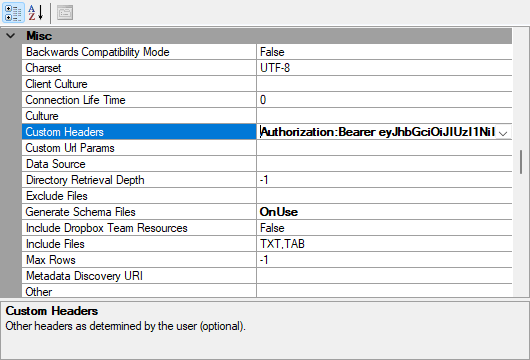
How it is stated is really important, so a misplaced blank space or incorrect case of a character will make it not work.
In some instances you would want to add more than one and that is also possible as you can hit the enter button to create a new row. Like so:
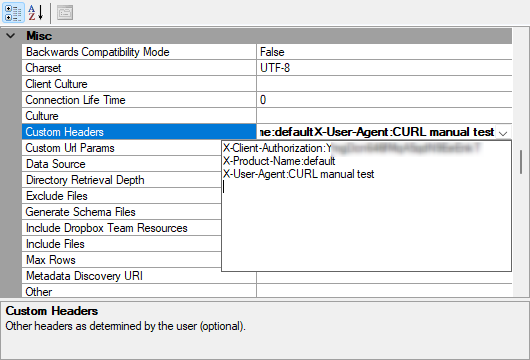
Using Custom URL Parameters
If the url you put in the URI field has a ? and some parameters after this, like so:
http://gorest.co.in/public-api/users?_format=json&page=1&per_page=100
Then you can move those after that sign into the custom url params field. The difference is that you need to use a comma between each parameter instead of a & sign. Like so.
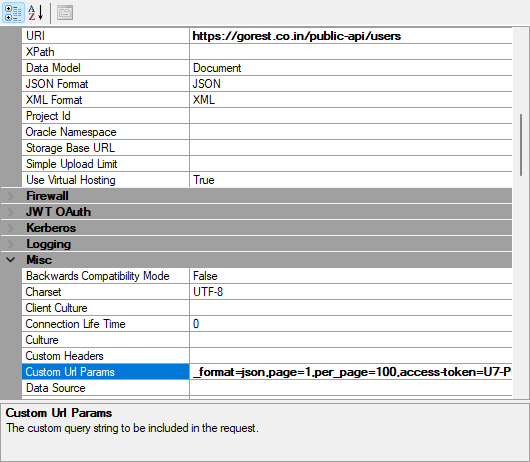
It will generate the same get url in the end.
Generating an RSD file
There now is a specific RSD guide available that shows all possible methods of doing this.
OAuth Authentication
The following is based on what can be found here Using OAuth there is some shared things to know. It will become an bearer token, which can also be used in a different non dynamic way.
Update From version 20.0.7593.0 and forward you will need to set the Auth Scheme to be OAuth so it is possible to actually use this option.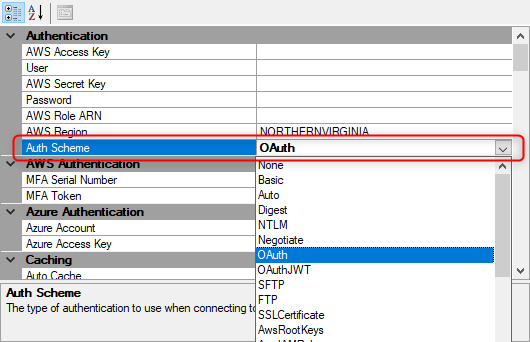
Following this you need to have Initiate OAuth set to GETANDREFRESH. OAuth Version needs to be set to what version of this the API is using, normally 2.0. You will also sometimes need to use an Callback URL, but it depends, when that is http://localhost:33333 is usually the one you should use. You need an OAuth Authorization Token URL or an OAuth Access Token URL, both and an OAuth Refresh Token URL. Sometimes also an OAuth Request token URL. All these can be different or the same URL.
Notice I don't mention that you should add the tokens to the available fields. That is because these tokens will be stored in the OAuthSettings.txt file, as encrypted data, after you click on the Authorize OAuth button.
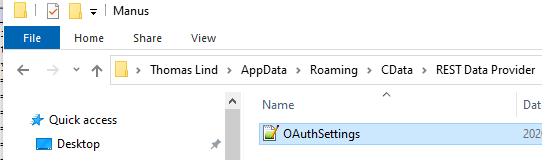
Consider overwriting the default location of the file with a specified location. This will make it work better when using scheduled execution and multiple users. If a new user connects to the file it will look at this persons AppData folder and locate no settings file if it is not specified with a fixed path.
Also be sure users are allowed to change the content of this folder so other users can update the tokens.
Following that you should change the Initiate OAuth to REFRESH and it will automatically update the tokens in the file when they are about to expire.
There are three methods to connect with, that are controlled by the OAuth Grant Type option.
Code
The Code option is the default method and the most common one. It requires an OAuth Client ID, OAuth Secret ID, OAuth Access Token URL and OAuth Authorization Token URL. As you can see below.
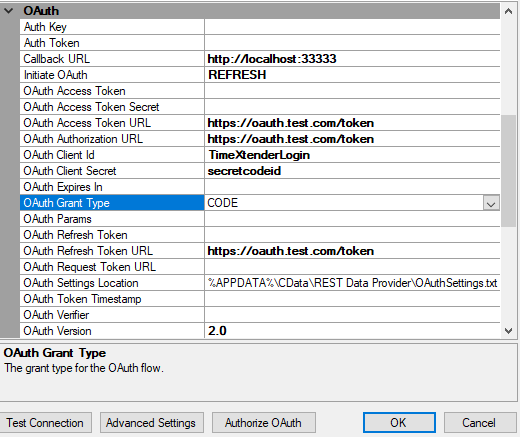
For a working guide we now have a specific guide for how to connect to Spotify here Authenticate using OAuth 2.0
Client
The Client method requires some other things, though seemingly the same. It doesn't require the Authorization Token URL, but instead will require some possible parameters in the OAuth Params field as the one below does.
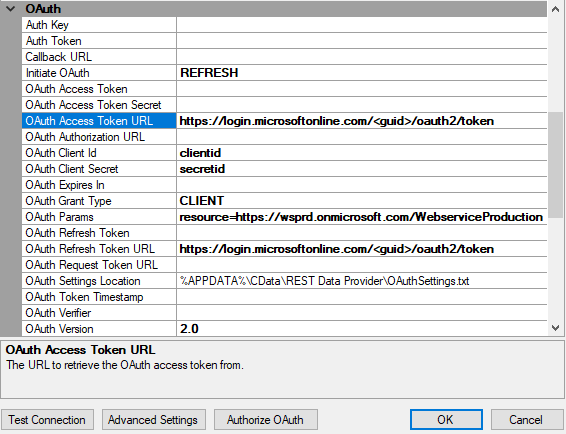
Regarding parameters you will at times have to add more than one type. For example you could have to add a scope and a state parameter. In that case it would look like so scope=okta.users.read,state=top. You split the individual types with an , sign and set the type equal an value.
Password
Finally there also is an Password method. It is similar to the others, in that it requires an Access Token URL and an Refresh Token URL, the difference is that it uses an User and Password instead of client and secret. Notice that these fields are in the "Authentication" section, not in the area of the other OAuth fields.
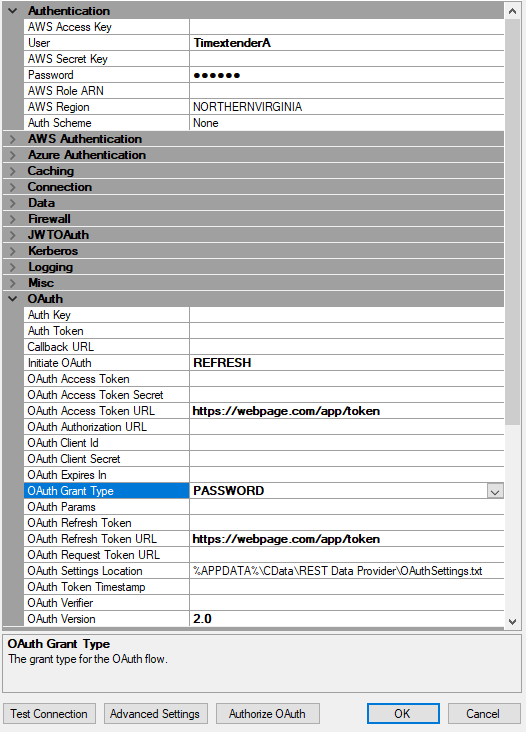
Advanced features
Automatically getting the correct data types
As standard CData will scan the first 100 rows and determine what data types these fields are. Sometimes this gives an error because the 101 row contained a longer string than was present in the previous rows. The solution simply is to change the Row Scan Depth field to a higher number. If you set it to 0 it will parse the whole file. Also in regards to JSON/XML files, this field doesn't only solve the issue of data type, but also what tables are available. If the file contains more than 100 rows in total these will not be added. So a good idea is to work out what the maximum amount of rows that are contained in the file and then add that or set it to 0 to be sure.
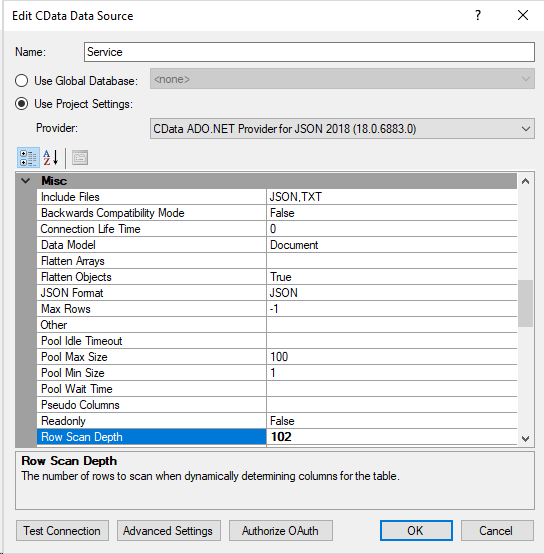
If, after you adjust the Row Scan Depth, you are still having issues with data types. You can set the Type Detection Scheme parameter to None. This will prevent the provider from attempting to detect the data types and simply bring in every field as a VarChar.
Parsing hierarchical data
Is exactly the same as in JSON or XML respectively. So you use the Data Model feature to choose what should be done with the data.
Using JSON Format
This is the same as in the JSON guide, the only difference is that you need to manually type in LDJSON to the field to use that option.
Pagination
There is now a specific RSD and pagination guide here
Creating and using RSD files for CData providers
0 Comments